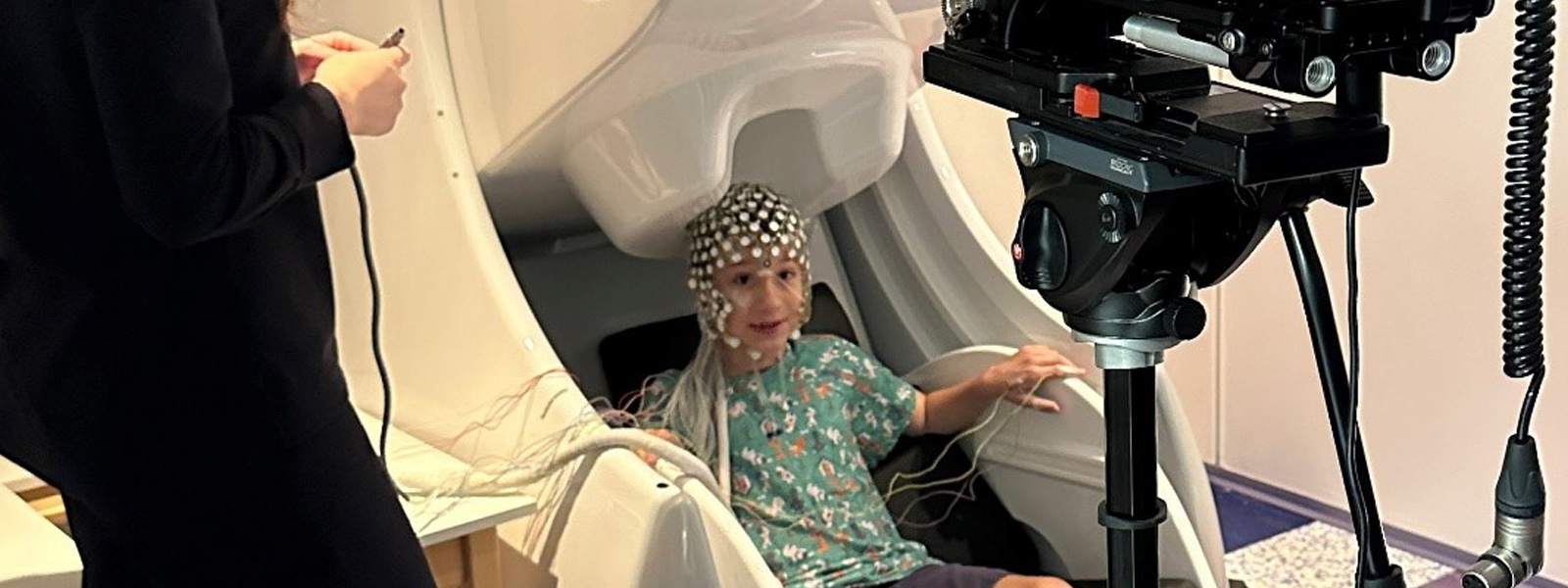
Published research: Electromagnetic imaging for children with drug-resistant epilepsy
Christos Papadelis, Ph.D., Assistant Vice President of Neuroscience Research, and his team recently published an article in the Journal of Visualized Experiments, entitled "Electromagnetic Source Imaging in Presurgical Evaluation of Children with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy." Ludovica Corona, Ph.D., a postdoctoral research fellow, serves as first author in this study.
For children with drug-resistant epilepsy, seizure freedom relies on the delineation and resection (or ablation/disconnection) of the epileptogenic zone while preserving the eloquent brain areas. The development of a reliable and noninvasive localization method that provides clinically useful information for the localization of the epileptogenic zone is, therefore, crucial to achieving successful surgical outcomes. Electric and magnetic source imaging have been increasingly utilized in the presurgical evaluation of these patients showing promising findings in the delineation of epileptogenic as well as eloquent brain areas. Moreover, the combination of these two methods into a single solution, namely electromagnetic source imaging, performed on simultaneous high-density electroencephalography (HD-EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) recordings has shown higher source localization accuracy than either modality alone. Despite these encouraging findings, such techniques are performed in only a few tertiary epilepsy centers, rarely are recorded simultaneously, and are underutilized in pediatric cohorts. This study illustrates the experimental setup for recording simultaneous MEG and HD-EEG data as well as the methodological framework for analyzing these data aiming to localize the irritative zone, the seizure onset zone, and eloquent brain areas in children with drug-resistant epilepsy. The publication is accompanied by an educational video presenting the steps of this experimental setup. The proposed framework would help other epilepsy centers to adopt the novel and unique neuroimaging techniques developed and used at Cook Children’s Medical Center for improving the presurgical evaluation of children with drug-resistant epilepsy.
The study is funded by Dr. Papadelis' R01 grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.